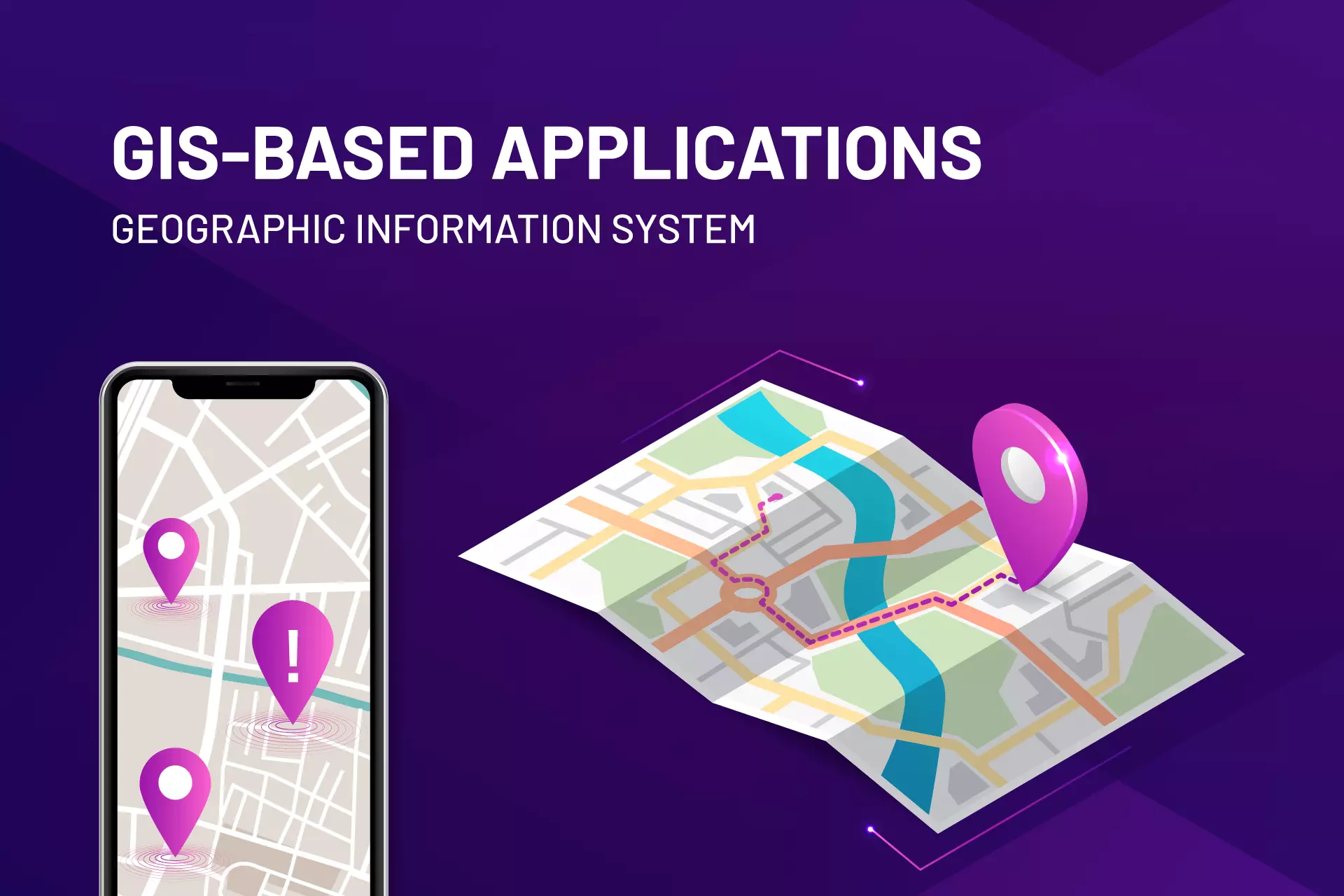
Applications based on geographic information system (GIS) are constantly upgrading as their applications in various sectors increase. Also, GIS-based systems have a vital role in digital transformation from command-line, workstation-based software to geospatial tools used on mobile devices and in the cloud for over twenty years. Moreover, it is essential to serve mass users to precisely locate, deliver or track the action through the system.
What is Geographic Information System?
A system for the creation, management, analysis, and mapping of all kinds of data is a geographic information system (GIS). Therefore, GIS helps data to connect with a map, which combines location data (where things are) with all kinds of descriptive information. Also, GIS provides a foundation for mapping and analysis, utilized in almost every industry and scientific discipline. GIS enables users to comprehend patterns, relationships, and the context of a given location. Additionally, the advantages include improved management and decision-making and enhanced communication and efficiency.
In 1854, in London City, no computers got used to map a disease outbreak. This kind of spatial analysis gets still used today, albeit in a more sophisticated manner.
Without a spatial reference, data doesn’t give a sense of where you are. Additionally, it is impossible to comprehend the present-day world with no geographic context.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are necessary for this reason, and you may not be aware of how much of an impact they have on our day-to-day lives.
What Does Geographic Information System (GIS-based application) Do?
GIS functions on multiple levels. For example, computer cartography, or simple mapmaking, is the most fundamental use of geographic information systems technology.
Similarly, GIS got used by hundreds of thousands of organizations worldwide to create maps that solve complex problems, perform analysis, communicate, and share information. The world is changing as a result of this.
GIS is used for:
- Problem-solving,
- Monitoring change,
- Managing and responding to events,
- Forecasting,
- Setting priorities, and
- Understanding trends.
Geographic Information System Cartography
Any GIS analysis typically produces a map as its final product. It could be a printed map or an online mapping software such as ArcGIS Online.
Geographic Information System Maps
Once all of the desired data gets entered into a GIS system, they combine to create a wide range of distinct maps, each with its own set of data layers. Comparing natural features to human activity is one of the most common applications of GIS technology.
GIS maps, for instance, can show which artificial features are close to particular natural characteristics, such as which homes and businesses are in flood-prone areas.
How does Geographic Information System mapping work?
GIS mapping results in the visualization of spatial data. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) get based on four fundamental ideas:
- Make use of geographic data.
- Utilize a database to manage it.
- Look for patterns through analysis.
- Plan it out on a map.
We can make better decisions with GIS because how we view and analyze data on maps affects how we understand the data.
It helps us comprehend where everything is. The analysis gets easier. The answers become apparent.
Because until you see how your data relates to other things in a geographic context, you won’t be clear about it.
GIS Jobs
People working in many different fields use GIS technology, e.g., scientific investigations, resource management, and development planning can all benefit from GIS technology.
Likewise, GIS is used by many retail businesses to find new locations for their stores. Marketing firms use GIS to determine who and where to advertise stores and restaurants.
What are the Geographic Information System Use Cases?
Millions of decisions around the world are based on GIS every day. You may not even be aware of how much it affects our lives. We use GIS, for instance, for:
- Identifying new store locations,
- Reporting power outages,
- Analyzing crime trends, and
- Using car navigation to plan your route
Components of a Geographic Information System (GIS-based application)
The three primary components of a geographic information system are as follows:
Data
GIS stores data on locations in the form of thematic layers. An attribute table contains information about the feature in each data set. Raster and vector data are the two main types of GIS data:
Raster
Because they store data in rows and columns, raster data resemble grids. They can be continuous or discrete. We frequently use raster data to represent imagery, temperature data, and land cover.
Vectors
Points, lines, and polygons with vertices are all examples of vectors. Vectors include, for instance, contours, administrative boundaries, and fire hydrants frequently.
Hardware
GIS software runs by hardware. It could be anything from mobile phones to powerful servers to a private GIS workstation. Data processing is the goal, and your workhorse is the central processing unit (CPU). In GIS, additional storage, dual monitors, and sharp graphic processing cards are also essential.
Software
ArcGIS and QGIS are the most popular GIS software programs. The application of math to maps in spatial analysis is the focus of GIS software. Therefore, it uses modern technology and geography to measure, quantify, and comprehend our world.
Careers in Geographic Information System (GIS-based application)
This percentage has decreased to 60% thanks to GIS researcher careers. Regardless, geography plays a significant role in data.
Spatial thinkers require a variety of tasks, including pipeline planning and ship navigation. Because of this, Geographic Information Systems get used in a wide range of fields. GIS jobs are in high demand for:
Digital Cartographers: Maps get prepared by cartographers. They require a bachelor’s degree in programming specializing in cartography, geography, geomatics, or surveying.
Database managers: Data is stored and extracted from structured sets by database managers into spatial databases.
Programmers automate redundant GIS processes and write code. Python, SQL, C++, Visual Basic, and JavaScript are a few examples of GIS programming languages.
In addition, Specialists in Remote Sensing utilize aerial, satellite, and remote sensing software. Therefore, Spatial analysts use geoprocessing tools to manipulate, extract, locate, and analyze geographical data. Furthermore, Land Surveyors measure the three-dimensional coordinates of the land.
The GIS process cannot function without well-trained professionals proficient in spatial analysis and GIS software. So, the aspect of people consists of three elements: networking, career path, and education. Therefore, attending conferences, looking for a GIS internship, and taking classes can all help someone build a career in GIS.
It’s essential to pick the right GIS job. If you haven’t taken the necessary programming classes, you shouldn’t try to get a job as a GIS developer if you are very good at GIS analysis.
Lastly, maintaining ongoing connections with other GIS professionals is essential for exchanging ideas and developing a support network.